# Heading
138.复制带随机指针的链表 (opens new window)
Tags: algorithms amazon bloomberg microsoft uber hash-table linked-list
Langs: c cpp csharp golang java javascript kotlin php python python3 ruby scala swift typescript
- algorithms
- Medium (59.46%)
- Likes: 468
- Dislikes: -
- Total Accepted: 57.3K
- Total Submissions: 96.4K
- Testcase Example: '[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]'
给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
要求返回这个链表的 深拷贝。
我们用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示Node.val的整数。random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从0到n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为null。
示例 1:
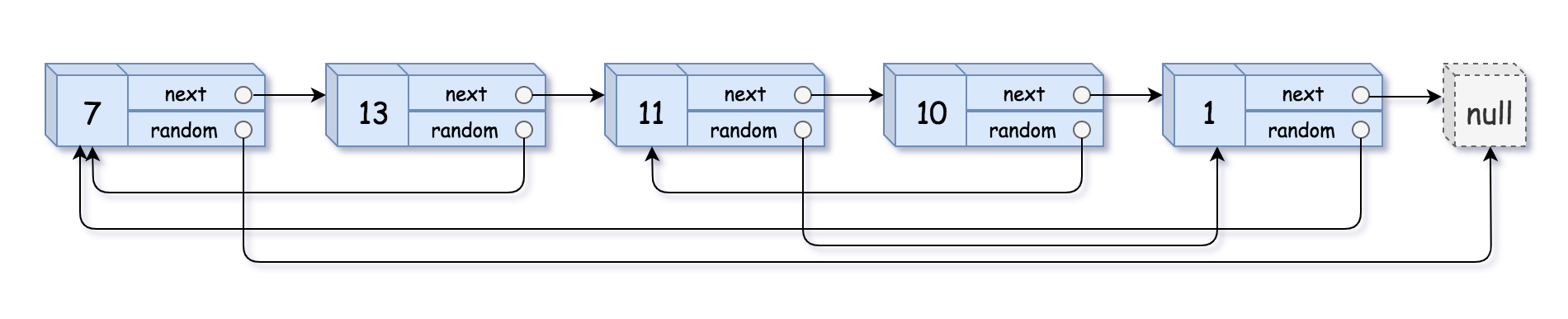
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] 输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
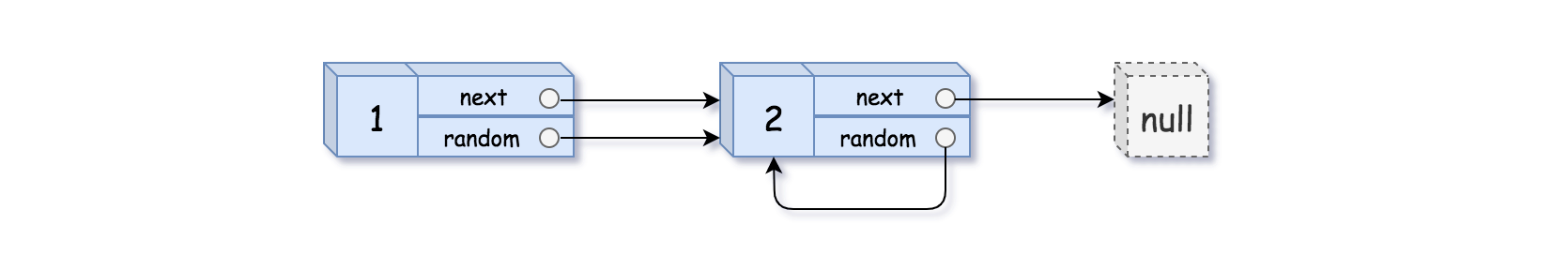
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]] 输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
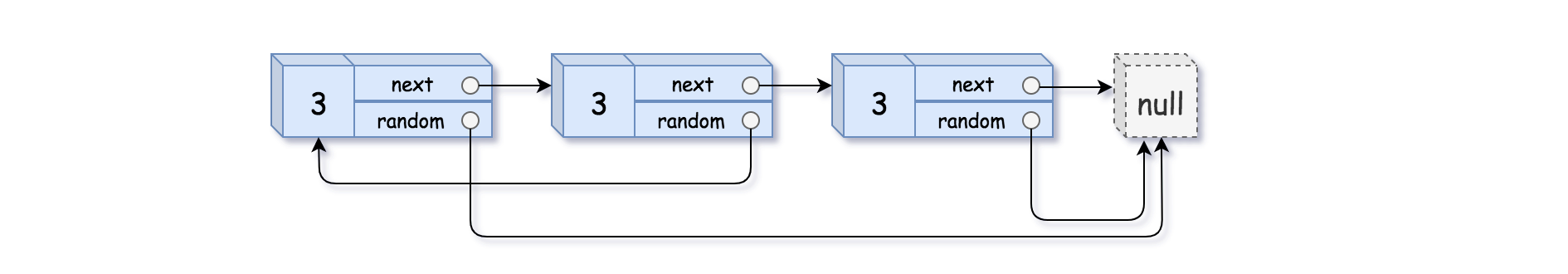
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]] 输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
示例 4:
输入:head = [] 输出:[] 解释:给定的链表为空(空指针),因此返回 null。
提示:
-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000Node.random为空(null)或指向链表中的节点。- 节点数目不超过 1000 。
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=138 lang=javascript
*
* [138] 复制带随机指针的链表
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* // Definition for a Node.
* function Node(val, next, random) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* this.random = random;
* };
*/
/**
* @param {Node} head
* @return {Node}
*/
var copyRandomList = function(head) {
if(head == null) return null;
let p = head;//扫描指针
const nodeList = [];
let q;//尾指针
while(p){
let node = new Node(p.val,null,p.random);
if(q){
q.next = node;
}
q = node;
nodeList.push(node);
p = p.next;
}
p = head;
let i = 0;
while(p){
for(let j = 0; j < nodeList.length; j++){
if(nodeList[j].random === p){
nodeList[j].random = nodeList[i];
}
}
i++;
p = p.next;
}
return nodeList[0];
};
/**
* @param {Node} head
* @return {Node}
* 优化一下,使用map存储对应关系 98%
*/
var copyRandomList = function (head) {
if (head === null) return null;
const indexMap = new Map();//存储原始节点的下标
let p = head,
i = 0, tmpNode;
let nodeArr = [];
//创建节点,维护val值
while (p) {
tmpNode = new Node(p.val, null, p.random);
nodeArr.push(tmpNode);
indexMap.set(p, i++);
p = p.next;
}
//维护next指针和random指针
let randomIdx;//原始随机节点的下标
nodeArr.forEach((node, index) => {
randomIdx = indexMap.get(node.random);
node.next = nodeArr[index + 1] || null;
node.random = nodeArr[randomIdx] || null;
})
return nodeArr[0]
};
/**
* @param {Node} head
* @return {Node}
* 进一步优化,遍历一次
*/
var copyRandomList = function (head) {
if (head === null) return null;
const nodeMap = new Map();//存储原始节点和新节点的对应关系
let p = head,
tmpNode;
let hair = new Node(),//头结点
tail = hair,//尾指针
randomNode;
//尾插法创建节点,维护当前节点的val、random和上一节点的next
while (p) {
if (!p.random) {
randomNode = null;
} else if (nodeMap.has(p.random)) {
randomNode = nodeMap.get(p.random);
} else {
randomNode = new Node(p.random.val);
nodeMap.set(p.random, randomNode);
}
tmpNode = nodeMap.has(p) ? nodeMap.get(p) : new Node(p.val);
tmpNode.random = randomNode;
nodeMap.set(p, tmpNode);
tail.next = tmpNode;
tail = tmpNode;
p = p.next;
}
return hair.next;
};
// 有个很清奇的思路(官方方法三):
// 每个原始节点后面复制一个节点,新节点random指针就是旧节点random.next,最后再将新旧节点拆分。
// 可以看这个解释加强理解:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/solution/javatu-jie-cong-hashmapdao-chang-shu-kong-jian-by-/
// @lc code=end
// @after-stub-for-debug-begin
module.exports = copyRandomList;
// @after-stub-for-debug-end1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
